Normally the PCB design current will not exceed 10A or even 5A. Especially in home and consumer electronics, the continuous working current on PCB usually does not exceed 2A. However, to power the company's product design recently, the continuous current can reach around 80A. Considering the instantaneous current and leaving a surplus for the whole system, the continuous current of power line should be able to withstand more than 100A. So the question is, what kind of PCB can withstand 100A current?
To understand the overcurrent capacity of PCB, we start with the PCB structure. In the case of a double-layer PCB, this type of printed circuit board is usually a three-layer structure: copper sheet, plate, and copper sheet. Copper skin is the path through which current and signal in PCB pass. According to middle school physical knowledge, it is known that the resistance of an object is related to material, cross-section area and length. Since our current moves on the copper sheet, the resistivity is fixed. The cross-sectional area can be seen as the thickness of the copper sheet, which is the thickness of the copper in the PCB processing options. Usually the copper thickness is expressed as OZ, the equivalent of 1OZ is 35um, the value of 2OZ is 70um, and so on. It is then easy to conclude that when a large current is passed through a PCB, the wiring will be short and thick, and the thicker the copper, the better.
In practice, there is no strict standard for the length of the wiring in engineering. Three indicators, copper thickness/temperature rise/line diameter, are commonly used in engineering to measure the current carrying capacity of PCB boards. The following two tables are available for reference:
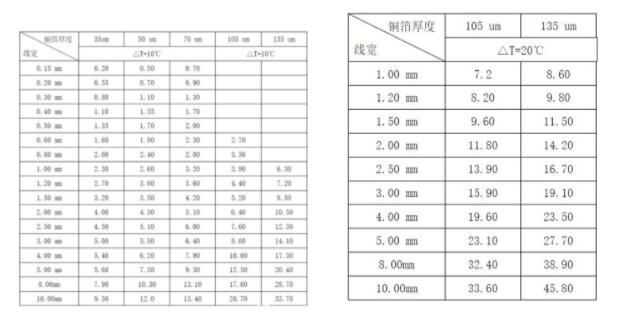
It can be seen from the table that a 1 Oz copper thick circuit board can pass a current of 4.5A through a 100 Mil (2.5mm) width wire at 10 degrees temperature rise. As the width increases, the current carrying capacity of PCB does not increase linearly, but decreases gradually, which is also consistent with the actual project. If the temperature rises, the current carrying capacity of the conductor can also be improved.
The PCB wiring experience obtained from these two tables is that increasing the copper thickness, widening the line diameter, and increasing the heat dissipation of PCB can enhance the current carrying capacity of PCB.
So if I want to go 100A current, I can choose 4Oz copper thickness, 15mm width, double-sided line, and increase the heat sink, reduce the temperature rise of PCB, and improve stability.
In addition to traveling on PCB, it can also be traveled by connecting posts.
Fix several 100A-resistant terminals on the PCB or product housing, such as surface nut, PCB terminals, copper columns, etc. Then connect 100A-capable wires to the terminal using connectors such as a copper nose. This allows a large current to travel through the wire.
Even the brass bars can be customized. It is a common practice in industry to use bronze plates for high current, such as transformers, server cabinets, etc.
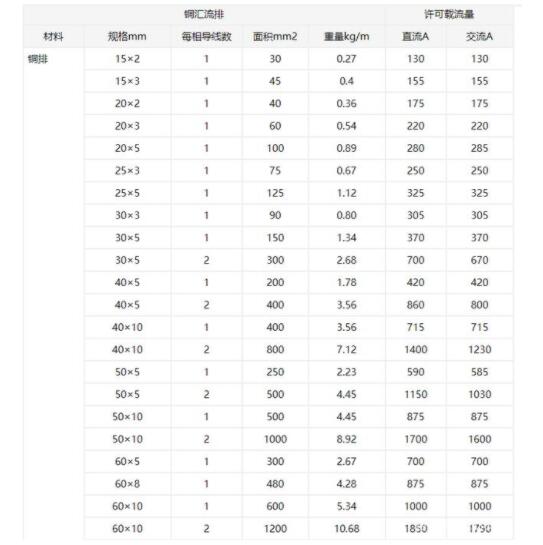
Attached bronze current carrying capacity table
There are also some special PCB processes, domestic PCB manufacturer may not be able to find processing. Infineon has a PCB with three layers of copper. The top and bottom layers are the signal wiring layers, and the middle layer is the 1.5mm thick copper layer, which is specially designed for power supply. This PCB can easily achieve small volume over 100A.