How to identify variable resistors in PCB circuit boards
With the development of high-voltage variable resistance technology in the mid-1970s, metal oxide variable resistance arresters almost completely replaced the old-fashioned overvoltage protection devices in the power supply network. The variable resistance arrester can safely convert the strong lightning impulse voltage and operating transient overvoltage that occurs on the overhead line to the ground, assist or replace the lightning protection line, and improve the power quality and the operating characteristics of the entire line.
Metal oxide varistor arresters use modern materials and protection technology to strictly control the voltage-related nonlinear operating parameters, and these parameters can be set during the manufacturing process. This means that the device can be selected accurately and provide safety and higher education protection according to specific requirements, so that it can operate in any voltage level of the power transmission and distribution system, and even in some extreme environmental conditions, such as lightning disaster areas or Severely polluted areas, etc.
What is the role of variable resistors?
The variable resistor is an adjustable electronic component. It is composed of a resistor body and a rotating or sliding system.
Variable resistors, resistors whose resistance can be adjusted, are used where the circuit current needs to be adjusted or the circuit resistance needs to be changed. The variable resistor can change the characteristics of the signal generator, dim the light, start the motor or control its speed.
It is mainly by changing its own resistance to control the current in the series circuit, which can protect some electrical components (requirements for current magnitude).
Variable resistors are usually used in circuits that require frequent adjustment (that is, the resistance does not need to change frequently). They play the role of adjusting voltage, adjusting current or signal control, and their main parameters are basically the same as fixed resistors.
Depending on the application, the resistance material of the variable resistor can be metal wire, metal sheet, carbon film or conductive liquid. For general currents, metal-type variable resistors are commonly used. In the case of very small current, the carbon film type is used. When the current is large, the electrolytic type is suitable; the electrodes of this variable resistor are all immersed in the conductive liquid. The potentiometer is a special form of variable resistor, which balances the unknown voltage or unknown potential, thereby measuring the unknown voltage or unknown potential difference. The more commonly used potentiometer is nothing more than a resistor with two fixed connectors, and the third connector is connected to an adjustable brush. Another use of the potentiometer is to use it as audio control in audio equipment.
Variable resistance is a kind of resistance first, it can play the role of resistance in electronic circuits. The difference between it and general resistance is that its resistance value can be continuously changed within a certain range. Variable resistors can be used for frequent changes. Due to the structure and use of variable resistors, the failure rate is significantly higher than that of ordinary resistors. Variable resistors are usually used in small-signal circuits, and large-signal variable resistors are also used in a few occasions such as tube amplifiers.
What are the types of variable resistors?
Variable resistors can be divided into: resistance box, sliding rheostat and potentiometer, etc.
The resistance box is a rheostat that can adjust the size of the resistance and display the resistance value. Compared with a sliding rheostat, a sliding rheostat cannot indicate the resistance value of the connected circuit, but it can continuously change the resistance in the connected circuit.
The sliding rheostat is made of resistance wire wound into a coil, and the length of the resistance wire connected to the circuit is changed by sliding the sliding sheet, thereby changing the resistance value. When connecting the circuit, it is generally connected in series and connected "one up and down", which is called current-limiting connection. There is also a connection method to connect three terminals, "two-one-one-up" connection, which becomes a partial pressure connection. This kind of connection will consume a lot of power, except for unavoidable circumstances, this connection is generally not used.
The potentiometer is a kind of adjustable resistance. It is usually composed of a resistor body and a rotating or sliding system, that is, a movable contact moves on the resistor body to obtain part of the voltage output.
Appearance feature
Variable resistors are very different from ordinary resistors in appearance. It has the following features, based on these features, variable resistors can be identified in the circuit board:
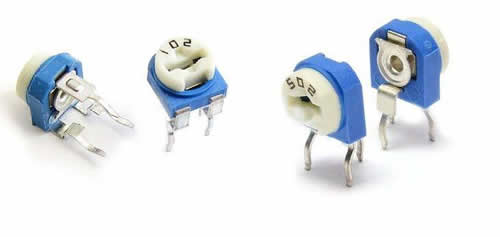
(1) The volume of the variable resistor is larger than that of the general resistor, and there are fewer variable resistors in the circuit, which can be easily found on the circuit board.
(2) There are three pins in the variable resistor. The three pins are different. One is the movable pin and the other two are the fixed pins. Generally, the two fixed pins can be used interchangeably. The pins of the fixed and movable plates cannot be used interchangeably.
(3) There is an adjustment port on the variable resistor. Use a flat-blade screwdriver to reach into this adjustment port. Turn the screwdriver to change the position of the moving piece and adjust the resistance.
(4) The nominal resistance value can be seen on the variable resistor. This nominal resistance value refers to the resistance value between two stator pins, which is also a certain stator pin and a moving piece pin. Resistance value between.
(5) Vertical variable resistors are mainly used in small signal circuits. Its three pins are vertically downward and mounted on the PCB circuit board vertically, and the resistance adjustment port is in the horizontal direction.
(6) Horizontal variable resistors are also used in small-signal circuits. Its three pins are at 90° to the resistance plane and are vertically downward. They are installed on the circuit board horizontally, with the resistance adjustment port facing upwards.
(7) The variable resistor of the small plastic case has a smaller volume and a circular structure. Its three pins are downward and the resistance adjustment port faces upward.
(8) The variable resistor (wire-wound structure) used in the occasion of high power has a large volume, and the movable piece can slide left and right to adjust the resistance value.