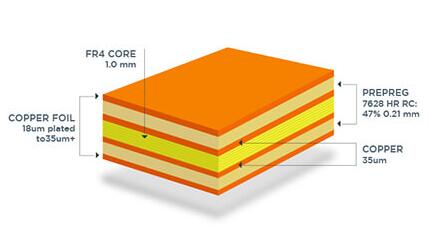
PCB is a board like electronic component that connects electronic components (wires, resistors, capacitors, etc.) to copper foil on a printed circuit board through chemical etching to form a circuit.
Packaging substrate refers to the packaging of electronic components (such as chips, resistors, capacitors, etc.) on a uniform substrate and fixing them together through processes such as soldering. The design and manufacture of the encapsulated substrate needs to take into account factors such as the layout of the components, the connection method, and the heat dissipation effect. It not only provides physical protection for the electronic components, but also provides a stable electrical connection for the circuit.
PCB substrates play a crucial role in electronic devices, providing electrical connections, mechanical support, and thermal management functions. By laying out and designing conductive trajectories, various complex circuit connections can be achieved, enabling the normal transmission of signals and currents between electronic components. At the same time, the structure and material selection of the PCB substrate can also provide sufficient mechanical strength and stability to support and protect electronic components. In addition, the PCB substrate can help disperse and conduct the heat generated, maintaining the normal operating temperature of electronic devices.
In summary, the PCB substrate is the core component of a printed circuit board, which achieves the connection, support, and thermal management functions of electronic components through its conductive trajectory and structure.
The difference between substrate and PCB
1. The substrate is the substrate of circuit components. As it is usually only used as a support for components, its structure and manufacturing process are relatively simple, and can be made into different shapes and sizes. On the contrary, PCBs are mainly used for manufacturing circuit connections, mainly to achieve conductivity and isolation of circuits. Therefore, their structure and manufacturing process are relatively complex and require higher accuracy and quality control. The main difference between substrates and PCB lies in the application environment and functionality, and their manufacturing processes are also different.
2. Different uses
The substrate is mainly used to support electronic components, while the circuit board achieves circuit connection and signal transmission of various components by coating the surface with conductive substances such as copper. Circuit boards can produce circuits of different levels and complexities, and can be used to manufacture various types of electronic devices, computer accessories, communication devices, etc. The substrate can be used in electronic devices such as LED displays that require large areas of flat support.
3. Different production processes
Substrate manufacturing generally adopts processes such as forming, stamping, drilling, copper coating, polishing, slotting, etc., while PCBs require more refined manufacturing processes such as etching and chemical copper plating. In addition, circuit boards also require wiring, welding, and other processes. The differences in manufacturing processes lead to differences in manufacturing costs and usage ranges, which also reflect the differences between them.
4. PCB is mainly used as a connector for electronic devices, used to connect various electronic components, such as chips, resistors, capacitors, etc.Substrate is mainly used on integrated circuit (IC) chips as a support and connecting material for the chips.
Although both packaging substrates and PCBs refer to the boards used to install and connect various electronic components in electronic devices, their uses, functions, and manufacturing processes vary greatly.