Rogers PCB materials have a low dielectric constant, typically between 2.2 and 3.5, which means they can maintain signal integrity and minimize signal loss at high frequencies and long distances.
The dielectric constant is the main parameter that reflects the dielectric or polarization properties of piezoelectric materials under the action of an electrostatic field. It is usually used ε To represent. Different types of piezoelectric components have different requirements for the dielectric constant of piezoelectric materials. When the shape and size of piezoelectric materials are constant, the dielectric constant ε Determined by measuring the inherent capacitance CP of piezoelectric materials.
The polarity of polymer materials can be determined based on their dielectric constant. Usually, substances with a relative dielectric constant greater than 3.6 are polar substances; Substances with a relative dielectric constant in the range of 2.8 to 3.6 are weakly polar substances; non-polar substances with a relative dielectric constant less than 2.8.
Relative dielectric constant ε R can be measured using an electrostatic field method: first, test the capacitance C0 of the capacitor when there is a vacuum between the two electrode plates. Then, measure the capacitance Cx using the same distance between the capacitor plates, but adding a dielectric between the plates.
The dielectric constant of common Rogers PCBs
1) RO4003C: 3.38
2) RO4350B: The dielectric constant (Dk: 3.48+/-0.05) has strict tolerance control and low loss characteristics (Df: 0.0037 10GHz).
3) RO5880:5880 sheet is a polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) based material with a dielectric constant of 2.2 and a thickness range of 0.003 inches to 0.240 inches. The copper foil thickness of the board can be selected as 0.5oz, 1oz, 2oz, and 3oz. Its dielectric constant has good stability, low loss, good impedance matching, and fast signal transmission speed. At the same time, the mechanical properties of the board are also very good, with characteristics such as high strength, high stiffness, good heat resistance, and chemical corrosion resistance.
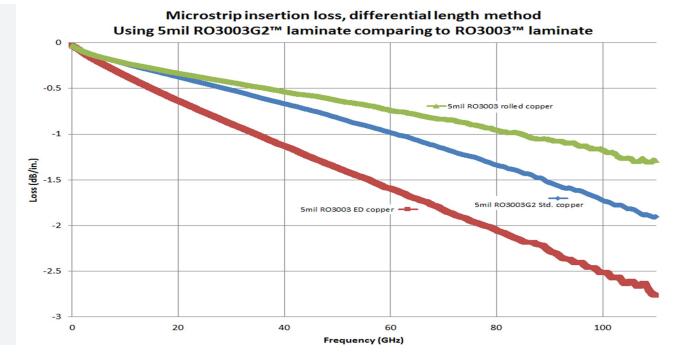
4) RO3003: The best resin and special filler were selected, as well as the ED copper material with extremely low copper foil surface roughness (lp). Its dielectric constants at 10GHz and 77GHz were 3.00 (clamp strip line method) and 3.07 (microstrip line differential phase method), respectively. The loss of Ro3003 high-frequency circuit board material is also very low. According to the differential length method of microstrip lines, the insertion loss at 77GHz on 5mil Ro3003 material is only 1.3dB/inch.
The influence of dielectric constant on Rogers PCB
The dielectric constant of Rogers PCB has a significant impact on the performance of a circuit board. Generally speaking, the larger the dielectric constant, the slower the signal transmission speed and the less noise interference. However, the dielectric constant can also affect issues such as capacitance size and signal reflection. Therefore, when designing a PCB, it is necessary to choose appropriate materials based on the usage situation to achieve better circuit performance.
Generally speaking, the dielectric constant is a quantity that characterizes the degree to which a medium attenuates electromagnetic waves. The larger the dielectric constant, the greater the substrate loss, and the stronger the attenuation of electromagnetic waves.
The Rogers PCB dielectric constant reflects the relative ability of a dielectric to store electrostatic energy in an electric field. For dielectric materials, the smaller the relative dielectric constant, the better the insulation.