The so-called V-cut means that the PCB manufacturer, according to the customer's drawing requirements, cuts a segmentation line at a specific position of the PCB in advance with a turntable cutter. The purpose is to facilitate the subsequent SMT circuit board assembly. -panel)” because its cut shape looks like an English [V] shape, hence the name.
The reason why V-Cut needs to be designed on the circuit board is that the circuit board (PCB) itself has a certain strength and hardness. If you want to open or break the PCB by hand, it is impossible, even if you It is the Hercules that can break it, and eventually the parts on the circuit board will be damaged. Therefore, this kind of pre-cut V-Cut circuit is needed to facilitate the operator to smoothly cut the original panel into a veneer. This is [De-panel].
The so-called V-cut refers to the printed circuit board (PCB) manufacturer according to the customer's drawing requirements, and cut the dividing lines in a specific position of the PCB with a rotary cutter in advance. The purpose is to facilitate subsequent SMT circuit board assembly. De-panel is used because its cut shape looks like an English [V] shape, hence the name.
Generally, the production of bare circuit boards will first do the panelization and break-away operations, so when the circuit board is printed (pasted) all the parts and the assembly is completed, it is of course necessary to carry out dividing.
Only when the board is installed in the machine can the board be installed in the machine, because usually the whole product does not install more than two identical assembly boards (PCBA). As for why the circuit board needs to be panelization and edge addition operations, Leave it to the next article to continue the explanation!
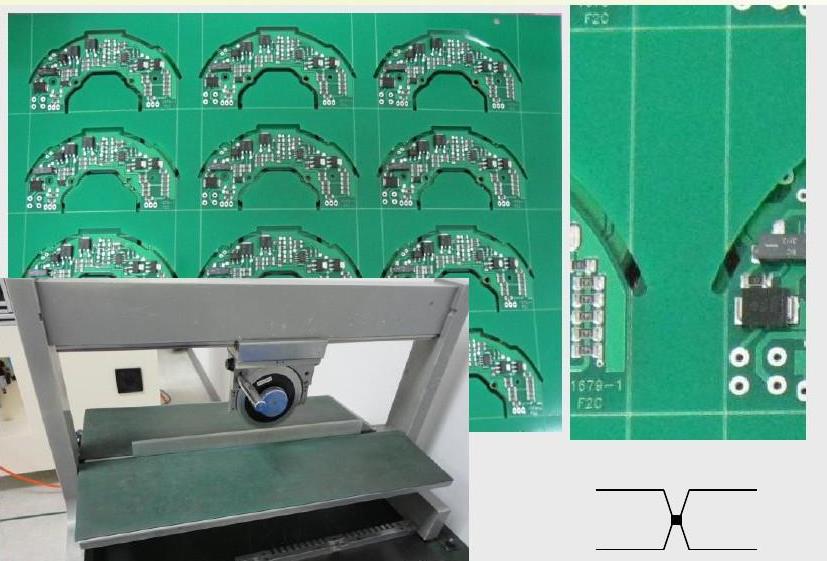
V-Cut PCB
The purpose of designing [V-cut] and the work of V-Cut splitting
As mentioned in the previous section, the main purpose of designing [V-cut] is to help the operator to de-panel the board after assembly of the circuit board. When PCBA is split, the [V-Cut board splitter] is generally used. (Scoring machine)], align the V-shaped grooves cut in advance on the PCB with the circular blade of Scoring, and then push it hard. Some machines have an automatic board feeding design. As long as a button is pressed, the blade will automatically move and Cut the board through the V-Cut position of the circuit board. The height of the blade can be adjusted up and down to meet the thickness of different V-Cut. (Note: In addition to using V-Cut's Scoring, there are other methods for PCBA splitting, such as routing, stamp hole... etc.)
Although the V-Cut on the PCB can also be manually broken or broken off the position of the V-Cut, do not use the manual method to break or break the V-Cut, because the manual way will cause the PCB due to the force point. Bending, it is very easy to cause cracks, micro-crack, electronic parts on the PCBA, especially capacitor parts, which will reduce the yield and reliability of the product. Some problems will gradually appear even after a period of use.
V-Cut design and use restrictions
Although V-Cut allows us to easily separate the board and remove the board edges, V-Cut has limitations in design and use.
First of all, V-Cut can only cut straight lines and cut to the end. That is to say, V-Cut can only cut into a line and cut straight from beginning to end. It cannot turn to change direction, nor can it cut a short section like a tailoring thread. Skip a short paragraph.
This is because the groove of the V-Cut is cut by a chainsaw with two upper and lower discs. I have seen a carpenter cutting wood, which means that it is probably like that, because the cutting of the PCB must be very precise ( Millimeter calculation), so we can’t do the job of cutting only half and withdrawing the knife. In fact, it is not impossible, but there is no need to spend a lot of time to do this. We only need to abandon the V-Cut splitting process and use Routing to remove the board. It can be achieved by cutting the board with a machine. So generally if it is a more complicated cutting path, routing machine will be used to split the board.
Secondly, the PCB thickness is too thin and it is not suitable for V-Cut groove. Generally, if the thickness of the board is less than 1.0mm, it is not recommended to make V-Cut. This is because the V-Cut groove will destroy the original PCB structural strength. When heavy parts are placed on the board with the V-Cut design, the board becomes easy to bend due to the relationship of gravity, which is very unfavorable for the SMT welding operation (easy to cause empty welding or short circuit).
In addition, when the PCB goes through the high temperature of the reflow furnace, the board itself will soften and deform due to the high temperature exceeding the glass transition temperature (Tg). If the V-Cut position and groove depth are not designed well, the PCB deformation will be more serious., It is unfavorable to the secondary reflow process.
What is V-Cut? Why is there a V-Cut on the PCB?
PCB V-Cut's residual thickness design and suggestions
Generally speaking, when we define the size of the V-Cut groove, we will only define the remaining thickness (Remained thickness), that is, the thickness of the remaining plate between the two inverted V ports of the V-Cut groove, because of this thickness Determines the severity of whether the board is easily broken and deformed.
The most common residual thickness of V-Cut is recommended to be 1/3 of the thickness of the board, but the minimum is not recommended to be less than 0.35mm. The thinner it is, the risk of premature breakage of the board during the manufacturing process is likely to occur. The maximum thickness of V-Cut is not recommended to be greater than 0.8mm. If it is thicker, the V-Cut cutting machine (Scoring) may not be able to completely cut it at one time, and it will increase the damage of the V-Cut cutting machine blade and reduce its service life.
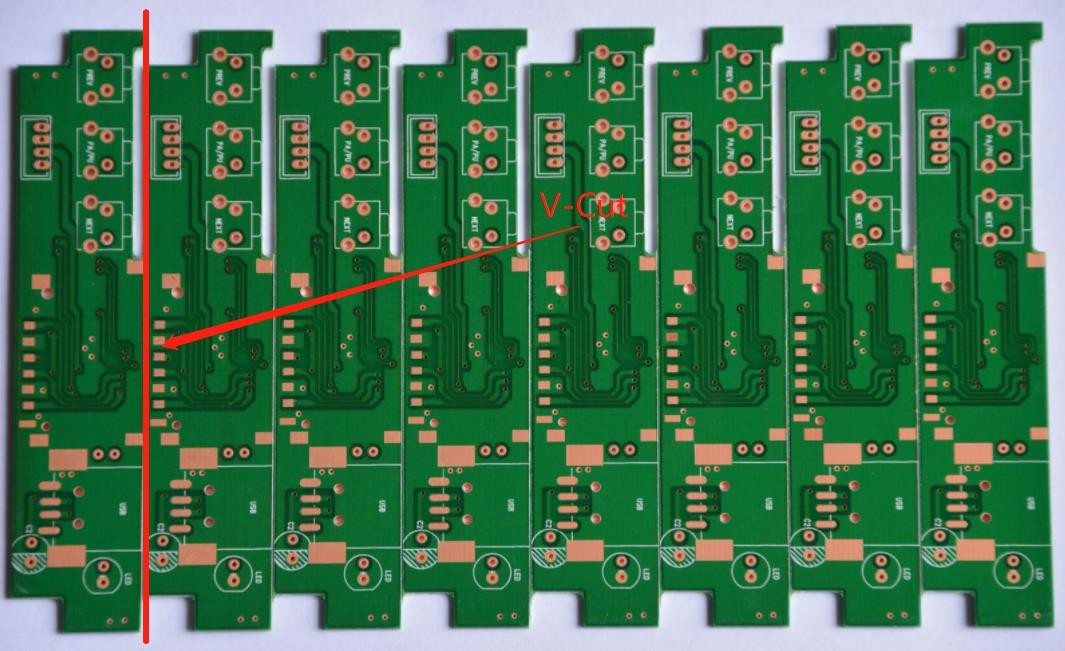
PCB V-Cut
Angle definition of PCB V-Cut
Finally, the V-shaped included angle of V-Cut is defined. Generally speaking, V-Cut has three angles of 30°, 45°, and 60°, and the most commonly used is 45°.
The greater the angle of the V-Cut, the more the board edge is eaten by the V-Cut. The circuit on the opposite PCB must be more retracted to avoid being cut by the V-Cut or cutting the V -Damage when Cut.
The smaller the angle of the V-Cut, the better PCB space design is theoretically, but it is not good for the life of the V-Cut saw blade of the PCB manufacturer, because the smaller the V-Cut angle, the thinner the blade of the electric saw. The thinner it is, the easier it is to wear and break its blade. In addition, when the thickness of the board is thicker, it must be cut deeper, so the angle of V-Cut generally has to be larger. If the board thickness is more than 1.6mm, the board factory is usually unwilling to accept the V-Cut PCB angle of 30°. -Cut angle, unless you are big enough, use Router cutting design instead.
Since Router cutting can almost solve all the disadvantages caused by V-Cut cutting, why design V-Cut? Because the price is different! This world is like this. There is absolutely no cheap and easy-to-use things. If you have one, you will be dominated, and there will be no other choices, right!