In addition to the traditional ADAS millimeter wave radar, the 4D millimeter wave radar with high resolution point cloud imaging capability has become the industry hotspot in recent two years for the high-precision perception needs of high-level automatic driving.
What is millimeter wave radar? Some giants and start-ups at home and abroad are focusing on this new concept product, with the goal of replacing or making up for the laser radar in some scenarios. Principle of vehicle mounted millimeter wave radar The vehicle mounted millimeter wave radar transmits millimeter wave outward through the antenna.
After all, the cost and reliability of laser radar are still difficult to land in recent stages, In severe weather such as rain and snow, millimeter wave radar is also required to perform the task of accurate and stable perception. Millimeter wave radar is a high-precision sensor to measure the relative distance, current speed and orientation of the measured object. The technical difficulty is still greatly improved compared with the traditional ADAS millimeter wave radar. What is millimeter wave radar? Millimeter wave refers to electromagnetic wave with a wavelength between 1-10mm. With short wavelength and wide frequency bands, it is easier to achieve narrow beam, and high radar resolution, and it is not vulnerable to interference. Millimeter wave radar is a high-precision sensor to measure the relative distance, current speed and orientation of the measured object. It was used in the military field in the early days. With the development and progress of radar technology, millimeter wave radar sensors began to be used in automotive electronics, unmanned aerial vehicles, intelligent transportation and other fields.
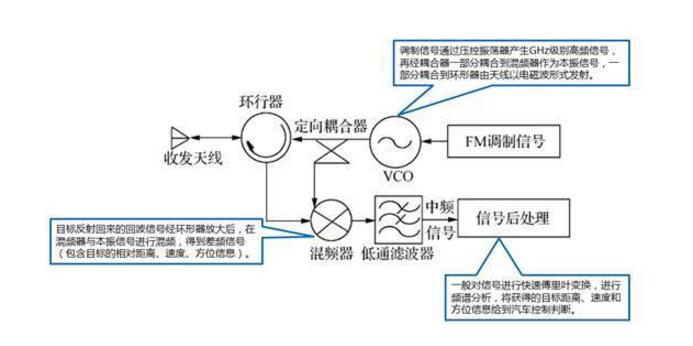
At present, different countries have different frequency bands assigned to vehicle mounted millimeter wave radars, but they mainly focus on 24GHz and 77GHz, and a few countries (such as Japan) use 60GHz. Due to the advantages of 77G over 24G, the frequency band of the global vehicle mounted millimeter wave radar will converge to the 77GHz band (76-81GHz) in the future.Principle of vehicle mounted millimeter wave radar The vehicle mounted millimeter wave radar transmits millimeter wave outward through the antenna, receives the reflected signal from the target, quickly and accurately obtains the physical environment information around the car body after post-processing (such as the relative distance, relative speed, angle, direction of movement, etc. between the car and other objects), and then tracks, identifies and classifies the target according to the detected object information, Then data fusion is carried out in combination with body dynamic information, and finally intelligent processing is carried out through the central processing unit (ECU). After reasonable decision, inform or warn the driver by sound, light, touch and other means, or timely make active intervention to the car, so as to ensure the safety and comfort of the driving process and reduce the probability of accidents.
On June 22, 1941, Nazi Germany was still unable to gain the air supremacy of the English Channel despite the loss of 1977 planes and 2585 pilots, let alone to disrupt the British ground and naval forces by air raids. It had to give up the "Sea Lion Plan" to invade Britain. The British air war that lasted more than a year ended in the defeat of Nazi Germany. The reason why Britain was able to withstand the attack of the German chariot and win the British air war (mainly because the chariot could not cross the sea) was that, in addition to the great role played by star fighters such as "Spitfire" and "Hurricane", there was also a great hero behind the scenes - the anti air radar called "Chain Home".
The first practical radar in the world was developed by Sir Robert Watson Watt, a British scientist and descendant of James Watt, who invented the steam engine. In order to give early warning to Nazi aircraft as early as possible, the British Air Force decided to deploy such radar in China on a large scale in May 1936, which is the prototype of the "local chain" radar. By the beginning of 1939, a total of 20 radar stations had been put into use. Before the implementation of the "Sea Lion Plan" of Nazi Germany, Britain had built two radar detection networks, with a total of 51 radar stations. These radars have made an important contribution to resisting the air attack of the German Air Force, and since then, the following 80 years of wide application of millimeter wave radars in various fields have begun.

Current development status of millimeter wave radar At present, millimeter wave radar is mainly 24GHz and 77GHz.
The 24GHz radar has a short measuring distance (5~30m), which is mainly used in the rear of cars; The 77GHz radar has a long measuring distance (30~70m) and is mainly used in the front and both sides of the car. Millimeter wave radar mainly includes three parts: radar RF front-end, signal processing system and back-end algorithm. Among the existing products, the patent licensing fees for the radar back-end algorithm account for about 50% of the cost, the RF front-end accounts for about 40% of the cost, and the signal processing system accounts for about 10% of the cost.
1. RF front-end RF front-end obtains IF signal by transmitting and receiving millimeter wave, and extracts distance, speed and other information from it. Therefore, the RF front-end directly determines the performance of the radar system. At present, the RF front-end of millimeter wave radar is mainly planar integrated circuit, which has two forms: hybrid microwave integrated circuit (HMIC) and monolithic microwave integrated circuit (MMIC). Among them, MMIC RF front-end has low cost and high yield, which is suitable for large-scale production. In terms of production process, epitaxial MESFET, HEMT, HBT and other device processes are generally used. Among them, GaAs based HEMT process is the most mature and has excellent noise performance.
2. Signal processing system The signal processing system is also an important part of the radar. By embedding different signal processing algorithms, it extracts IF signals collected from the RF front-end to obtain specific types of target information. The signal processing system generally uses DSP as the core to implement complex digital signal processing algorithms to meet the real-time requirements of radar.
3. Back end algorithm Back end algorithm accounts for the highest proportion of the cost of the whole millimeter wave radar. For millimeter wave radar, domestic researchers have proposed a large number of algorithms from the perspectives of frequency domain, time domain and time-frequency analysis, and the accuracy of offline experiments is also high. However, domestic radar products mainly use FFT based on frequency domain and its improved algorithm for analysis. The measurement accuracy and scope of application have certain limitations, while foreign algorithms are strictly protected by patents, and the price is very expensive.
In addition to the traditional ADAS millimeter wave radar, the 4D millimeter wave radar with high resolution point cloud imaging capability has become the industry hotspot in recent two years for the high-precision perception needs of high-level automatic driving. Some giants and start-ups at home and abroad are focusing on this new concept product, with the goal of replacing or making up for the laser radar in some scenarios. After all, the cost and reliability of laser radar are still difficult to land in recent stages, In severe weather such as rain and snow, millimeter wave radar is also required to perform the task of accurate and stable perception. The so-called 4D refers to 3D contour high-resolution point cloud contour and high-precision speed information. It is like concentrating the capabilities of the phased array radar on an aircraft carrier onto a radar the size of an Apple phone. The technical difficulty is still greatly improved compared with the traditional ADAS millimeter wave radar.
Millimeter wave radar has a broad market space. Due to the continuous improvement of vehicle safety standards in various countries, the Active Safety Technology Advanced Driving Assistance System (ADAS) has shown a rapid development trend in recent years. Automotive millimeter wave radar has become the mainstream choice recognized by automotive electronics manufacturers because it can work around the clock, and has huge market demand. In 2014, the global automotive millimeter wave radar market shipped 19 million. According to the prediction of Plunkeet Research, a market research institution, it is estimated that by 2020, the global automotive millimeter wave radar market will have nearly 70 million, and the compound annual growth rate from 2015 to 2020 will be about 24%. At present, the automotive millimeter wave radar market is mainly occupied by European and American manufacturers such as the mainland, Bosch, Wayking Weicheng, Haila, etc.