In our industry in recent years, the most fashionable technologies and products are HDI (High Density Interconnect) and Build-up MulTIlayer (Multilayer Printed Board). However, in the development trend of market economy and high-tech products, there is another branch, namely high-frequency microwave radio frequency printed boards and metal-based printed boards. Today, I will talk about these two issues.
1, let's talk about the high-frequency microwave radio frequency printed board
1. The high frequency microwave radio frequency printed circuit board is heating up on the land of China.
In recent years, many printed board companies in East China, North China, and the Pearl River Delta have been staring at the high-frequency microwave board market. Such new types of printed circuit boards are regarded as indispensable supporting products for the electronic information high-tech industry, and research and development should be strengthened. Some company bosses have identified high-frequency microwave boards as a new economic growth point for future enterprises.
Foreign experts predict that the market for high-frequency microwave panels will develop very quickly. In the fields of communications, medical care, military, automobiles, computers, and instruments, the demand for high-frequency microwave panels is rapidly rising. A few years later, high-frequency microwave boards may account for about 15% of the total global printed boards. Many PCB companies in Taiwan, South Korea, Europe, the United States, and Japan have formulated plans to develop in this direction.
European and American high-frequency microwave sheet suppliers Rogers, Arlon, Taconic, Metclad, GIL Japan Chukoh have entered the potential big market of China in the past two years, looking for agents and teaching related technologies. American GIL Company held a lecture on "Application and Manufacturing Technology of High Frequency Microwave and Radio Frequency Printed Boards" in Shenzhen. Hundreds of seats were fully occupied. The corridors were also full of business representatives to listen to the speech. Technical lectures all day long. I really didn't expect domestic counterparts to have such a strong interest in high-frequency boards. European and American sheet metal suppliers have been able to provide more than 100 varieties of sheet series with dielectric constants ranging from 2.10, 2.15, 2.17, ... to 4.5, and even higher.
In the Pearl River Delta and the Yangtze River Delta, it is understood that many companies have advertised that they can place bulk orders for Teflon and high-frequency boards. It is said that some companies have reached the level of monthly output of thousands of square meters. The demand for high-frequency microwave plates in many domestic radar and communications research institutes printed board factories is increasing year by year. Domestic companies such as Huawei, Bell, and Wuhan Institute of Posts and Telecommunications have been demanding high-frequency microwave printed circuit boards year by year. Foreign companies engaged in high-frequency microwave products have also moved to China to purchase printed circuit boards for high-frequency microwaves nearby.
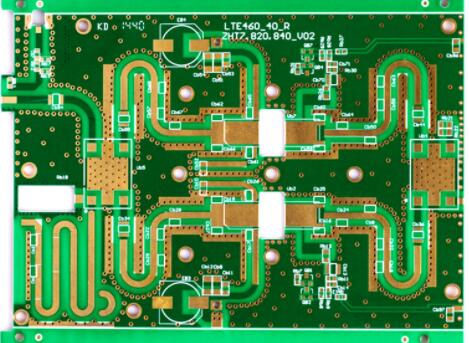
Various signs indicate that high-frequency microwave panels are heating up in China.
(What is a high-frequency board? Above 300MHZ, that is, the short-wave frequency range with a wavelength of more than 1 meter, generally called a high-frequency board.)
2. Why has the high frequency microwave board become hot in recent years?
There are three reasons.
1. The increase in computer technology processing capacity and the increase in information memory capacity, urgently require high-speed signal transmission.
2. Part of the frequency bands of high-frequency communications originally used for military purposes were given to civilian use (beginning in 1996), which greatly developed civilian high-frequency communications. It has demonstrated its skills in various fields such as long-distance high-speed communication, navigation, medical treatment, transportation, transportation, and storage.
3. High confidentiality and high transmission quality enable mobile phones, car phones, and wireless communications to develop towards high frequency, and high picture quality enables broadcast and television transmission to broadcast programs at VHF and UHF. High-volume information transmission requires satellite communications, microwave communications and optical fiber communications to be high-frequency.
In short, the high frequency and high speed of electronic information products put forward high requirements on the high frequency characteristics of printed boards.
3. ε of Teflon printed boards
Among printed circuit board substrates, PTFE has the lowest dielectric constant ε, typically only 2.6~2.7, while the FR4 dielectric constant ε of general glass cloth epoxy resin substrate is 4.6~ 5.0, therefore, the signal transmission speed of Teflon printed boards is much faster than FR4 (about 40%). The intermediate loss factor of Teflon board is 0.002, which is 10 times lower than the 0.02 of FR4, and the energy loss is much smaller. In addition, PTFE is called the "Plastic King". It has excellent electrical insulation properties, chemical stability and thermal stability (there is no solvent that can dissolve it below 300°C), so high-frequency and high-speed Signal transmission must first use Teflon or other low dielectric constant substrates. I have seen that Polyflon, Rogers, Taconic, Arlon, and Meclad can all provide substrates with dielectric constants of 2.10, 2.15, 2.17, and 2.20. The dielectric loss factor is 0.0005 to 0.0009 at 10GHZ. The performance of PTFE vinyl material is very good, but the process of its processing into a printed board is completely different from the traditional FR4 process. This aspect will be discussed later.
In the past two years, we have used Rogers RO4000 and GIL1000 series such as ε3.38, 3.0, 3.2, 3.8, etc. in practice in addition to those requiring ε of 2.15 and 2.6.
4. The basic requirements of high-frequency microwave panels
1. Warpage: 0.5~0.7% of the finished board is usually required.
2. Because it is high-frequency microwave radio frequency signal transmission, the characteristic impedance of the finished printed board conductor is required to be strict, and the line width of the PCB board is usually required to be ±0.02mm (the most stringent is ±0.015mm). Therefore, the etching process needs to be strictly controlled, and the film used for light imaging transfer needs to be compensated according to the line width and the thickness of the copper foil.
3. The circuit of this type of printed circuit board transmits not current, but high-frequency electrical pulse signals. Defects such as pits, gaps, and pinholes on the wires will affect the transmission, and any such small defects are not allowed. Sometimes, the thickness of the solder mask is also strictly controlled, and the solder mask on the circuit is too thick or too thin to be a few microns.
4. Heat shock at 288 degree Celsius, 10 seconds, 1~3 times, no pore wall separation occurs. For the PTFE board, the wettability in the hole must be solved, and the electroless copper hole has no holes, and the copper layer electroplated in the hole can withstand thermal shock. This is the difficulty of making a Teflon holed board. one. Because of this, many substrate manufacturers have developed and produced a higher ε, and the electroless copper process is the same as the conventional FR4 alternatives, RogersRo4003 (ε3.38) and LGC-046 (ε3.2±0.1) from Xi’an 704 Factory. It is this kind of product.
5. Why is the printed board required to have a low ε (Dk)?
ε or Dk, called the dielectric constant, is the ratio of the capacitance between electrodes filled with a certain substance to the capacitance of a vacuum capacitor of the same structure. It usually indicates the capacity of a certain material to store electrical energy. When ε is large, the ability to store electrical energy is large, and the transmission speed of electrical signals in the circuit will decrease. The current direction of the electrical signal through the printed board is usually positive and negative alternately, which is equivalent to the process of continuously charging and discharging the substrate. In the interchange, the capacitance will affect the transmission speed. This effect is even more important in high-speed transmission devices. Low ε means that the storage capacity is small, and the charging and discharging process is fast, so that the transmission speed is also fast. Therefore, in high-frequency transmission, a low dielectric constant is required.
Another concept is dielectric loss. Under the action of an alternating electric field, the energy consumed by the dielectric material due to heat is called the dielectric loss, which is usually expressed by the dielectric loss factor tanδ. ε and tanδ are proportional, and high-frequency circuits also require low ε and small dielectric loss tanδ, so the energy loss is also small.