The rigid-flex printed circuits board is likely to become a trap for novices on the road of new technology development. Therefore, it is very wise to know how to make flexible circuits and rigid-flex boards. In this way, we can easily find the hidden trouble in the design and take precautions. Now, let's know what basic materials are needed to make these boards.
First of all, let's consider the common rigid printed circuit boards, whose base materials are usually glass fiber and epoxy resin. In fact, these materials are a kind of fiber, although we call it "rigid", if you take out a single layer, you can still feel its elasticity. Because of the cured epoxy resin, it can make the board more rigid. Because it is not flexible enough, it can not be applied to some products. But it is suitable for many electronic products that are simply assembled and the board will not move continuously.
In more applications, we need more flexible plastic film than epoxy resin. Our most common material is polyimide (PI), which is very soft and firm. We can't tear it or extend it easily. Moreover, it has incredible thermal stability, and can easily withstand the temperature change during reflow soldering. Moreover, in the process of temperature fluctuation, we can hardly find its stretching deformation.
Polyester (PET) is another commonly used flexible circuit board material. Compared with polyimide (PI) film, its heat resistance and temperature deformation are worse than PI film. This material is often used in low-cost electronic devices, printed lines wrapped in a soft film. Because pet can't bear high temperature, let alone welding, it is usually made by cold pressing process. I remember that the display part of the clock radio uses this kind of flexible connection circuit, so the radio often does not work properly. The root cause is the poor quality connector. Therefore, we suggest that PI film should be selected for soft and hard bonding board, and other materials are available but not often used.
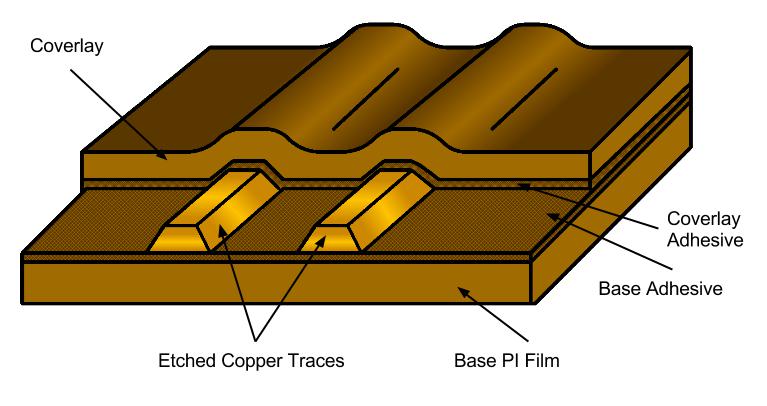
PI film, PET film, thin epoxy resin and glass fiber core are common materials for flexible circuits. In addition, the circuit also needs to use other protective film, usually PI or PET film, sometimes mask solder resist ink. The protective film can insulate the conductor from the outside and protect it from corrosion and damage. What is the thickness of PI and PET films? In the range of 1 to 3 mils, the thickness of 1 or 2 mils is commonly used. Glass fiber and epoxy are thicker, generally from 2 to 4 mils.
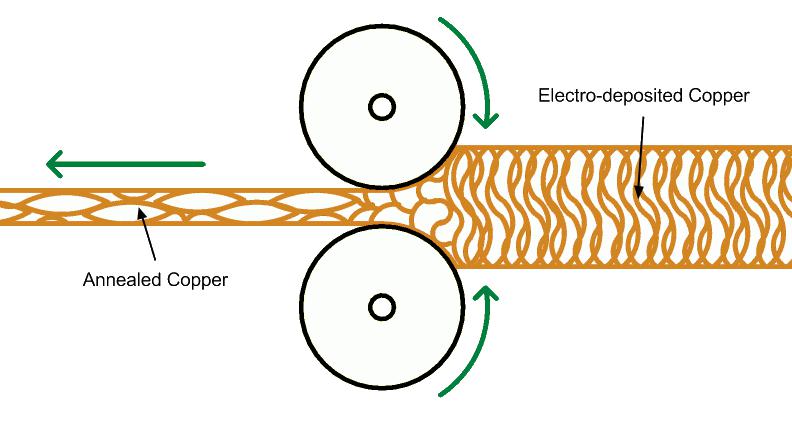
Printed wires, usually carbon film or silver based ink, are used in the above-mentioned cost-effective electronic products, but copper wires are still the common choice. According to different applications, we have to choose different forms of copper foil. If only in order to replace wires and connectors, so as to reduce the manufacturing time and cost, electrolytic copper foil is the best choice for stress circuit board. Electrolytic copper foil is also used to increase the current carrying capacity by increasing the weight of copper, so as to achieve the width of copper sheet, such as planar inductor.
As we all know, copper has always been poor in work hardening and stress fatigue. If the flexible circuit needs to be folded or shifted repeatedly in the final application, then high grade rolled toughened copper foil (RA) is a better choice. Obviously, more rolling toughening will increase the cost, but the rolling toughened copper foil can be bent and folded more times before fatigue fracture. And it's more elastic in the z-deflection direction, which is what we need. In the application of frequent bending and rolling, it gives us a longer life. Because the rolling toughening process elongates the grain structure in the plane direction. A typical example is the link between the bench and the milling cutter head, or the laser head in the Blue ray driver (as shown in the figure below).

In Blue ray machines, flexible circuits are used to connect the laser to the main circuit board. Please note that the flexible circuit on the circuit board on the laser head needs to be bent into a right angle. Here, a glue bead is used to enhance the connection of the flexible circuit.
Generally, we need adhesive to bond copper foil and PI film (or other films), because different from the traditional FR-4 rigid plate, there are not many burrs on the surface of rolled and toughened copper foil, so high temperature and high pressure can not achieve good adhesion. Manufacturers, such as DuPont, offer single, double-sided, corrosion-resistant copper clad laminates. It uses a thickness of ½ Mil or 1 mil acrylic or epoxy adhesive. This adhesive is specially developed for FPC. "Glue free" laminates are becoming more and more popular due to the introduction of new processes such as direct coating and deposition of copper on PI films. In HDI circuit boards that need finer spacing and smaller vias, the film can be used widely.
When we need to add protective beads to the soft and hard joint, we will use silicone, hot melt adhesive or epoxy resin. This will enhance the mechanical strength of the soft and hard joint, and ensure that there will be no stress fatigue or tearing in the process of reuse. The best example is shown in Figure 3.
It is very important to have a clear understanding of the materials used in flexible circuit boards or hard and soft circuit boards. We can also give them free choice of materials according to the application, but this will lay a hidden danger for the failure of the final product. Compared with my summary, Coombs, CF (editor in chief, 2008) printed circuit manual, 6th Edition, 2008 McGraw Hill, PP 61.30-61.24 describes the related contents in detail. Understanding the properties of materials can also help us design, evaluate and test the mechanical parts of products. If the research and development is applied to automotive products, then heat dissipation, moisture-proof, chemical corrosion, impact and other situations need to be carefully simulated, so as to use the correct materials to achieve high reliability and minimum allowable bending radius of the product. Ironically, we are driven to choose flexible board, which combines hard and soft board. In practice, it is often exposed to harsh environment. For example, low-cost consumer personal electronic devices are often troubled by vibration, falling, sweat and so on.