The inner layer production process of high-multilayer PCB
Due to the complex process flow of PCB manufacturing, in the planning and construction of intelligent manufacturing, it is necessary to consider the related work of process and management, and then carry out automation, information and intelligent layout.
1
Process classification
According to the number of PCB layers, it is divided into single-sided, double-sided, and multi-layer boards. The three board processes are not the same.
There is no inner layer process for single-sided and double-sided panels, basically cutting-drilling-follow-up process.
Multilayer boards will have internal processes
1) Single panel process flow
Cutting and edging - drilling - outer layer graphics - (full board gold plating) - etching - inspection - silk screen solder mask - (hot air leveling) - silk screen characters - shape processing - testing - inspection
2) Process flow of double-sided tin spraying board
Cutting edge grinding - drilling - heavy copper thickening - outer layer graphics - tin plating, etching tin removal - secondary drilling - inspection - screen printing solder mask - gold-plated plug - hot air leveling - silk screen characters - shape processing - testing - test
3) Double-sided nickel-gold plating process
Cutting edge grinding - drilling - heavy copper thickening - outer layer graphics - nickel plating, gold removal and etching - secondary drilling - inspection - silk screen solder mask - silk screen characters - shape processing - test - inspection
4) Process flow of multi-layer board tin spraying board
Cutting and grinding - drilling positioning holes - inner layer graphics - inner layer etching - inspection - blackening - lamination - drilling - heavy copper thickening - outer layer graphics - tin plating, etching tin removal - secondary drilling - inspection -Silk screen solder mask-Gold-plated plug-Hot air leveling-Silk screen characters-Shape processing-Test-Inspection
5) Process flow of nickel-gold plating on multilayer boards
Cutting and grinding - drilling positioning holes - inner layer graphics - inner layer etching - inspection - blackening - lamination - drilling - heavy copper thickening - outer layer graphics - gold plating, film removal and etching - secondary drilling - inspection - Screen printing solder mask-screen printing characters-shape processing-testing-inspection
6) Process flow of multi-layer plate immersion nickel-gold plate
Cutting and grinding - drilling positioning holes - inner layer graphics - inner layer etching - inspection - blackening - lamination - drilling - heavy copper thickening - outer layer graphics - tin plating, etching tin removal - secondary drilling - inspection -Silk screen solder mask-Chemical Immersion Nickel Gold-Silk screen characters-Shape processing-Test-Inspection.
2
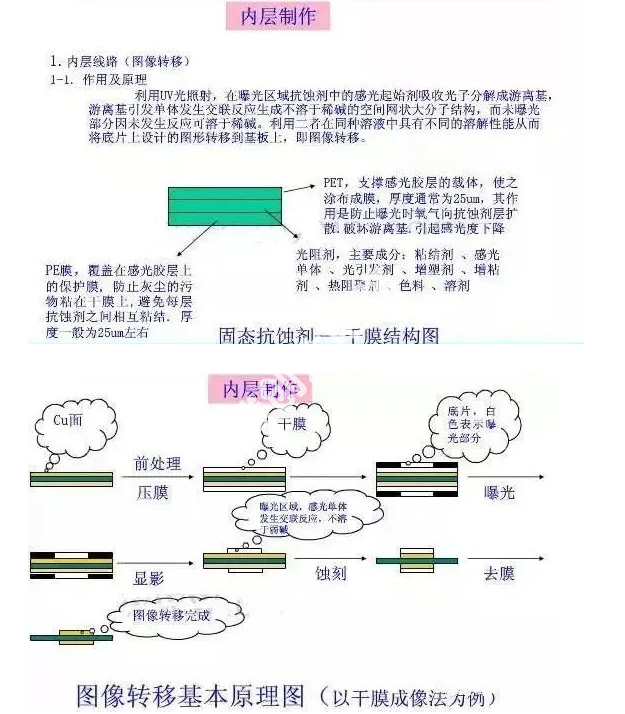
Inner layer production (graphic transfer)
Inner layer: cutting board, inner layer pre-processing, laminating, exposure, DES connection
Cutting (Board Cut)
1) Cutting board
Purpose: Cut the large material into the size specified by MI according to the requirements of the order (cut the substrate material to the size required by the work according to the planning requirements of the pre-production design)
Main raw materials: base plate, saw blade
The substrate is made of copper sheet and insulating laminate. There are different thickness specifications according to the requirements. According to the copper thickness, it can be divided into H/H, 1OZ/1OZ, 2OZ/2OZ, etc.
Precautions:
a. To avoid the influence of the board edge barry on the quality, after cutting, the edge will be polished and the corners will be rounded.
b. Considering the impact of expansion and contraction, the cutting board is baked before being sent to the process
c. Cutting must pay attention to the principle of consistent mechanical direction
Edging/rounding: mechanical polishing is used to remove the glass fibers left by the right angles of the four sides of the board during cutting, so as to reduce scratches/scratches on the board surface in the subsequent production process, which may cause quality hazards
Baking plate: remove water vapor and organic volatiles by baking, release internal stress, promote cross-linking reaction, and increase the dimensional stability, chemical stability and mechanical strength of the plate
Control points:
Sheet material: puzzle size, sheet thickness, sheet material type, copper thickness
Operation: baking time/temperature, stacking height
(2) Production of inner layer after cutting board
Function and principle:
The inner copper plate roughened by the grinding plate is dried by the grinding plate, and the dry film IW is attached, and then irradiated with UV light (ultraviolet rays). The exposed dry film becomes hard and cannot be dissolved in weak alkali, but can be dissolved in strong alkali. The unexposed part can be dissolved in weak alkali, and the inner layer circuit is to use the characteristics of the material to transfer the graphics to the copper surface, that is, image transfer.
Detail :(The photosensitive initiator in the resist in the exposed area absorbs photons and decomposes into free radicals. The free radicals initiate a cross-linking reaction of monomers to form a spatial network macromolecular structure that is insoluble in dilute alkali. It is soluble in dilute alkali when the reaction occurs.
The two have different dissolving properties in the same solution to transfer the pattern designed on the negative to the substrate to complete the image transfer).
The circuit pattern requires high temperature and humidity conditions, generally requiring a temperature of 22+/-3 degree Celsius and a humidity of 55+/-10% to prevent the film from deforming. The dust in the air is required to be high. With the increase in the density of the lines and the smaller the lines, the dust content is less than or equal to 10,000 or more.
Material introduction:
Dry film: Dry film photoresist for short is a water-soluble resist film. The thickness is generally 1.2mil, 1.5mil and 2mil. It is divided into three layers: polyester protective film, polyethylene diaphragm and photosensitive film. The function of the polyethylene diaphragm is to prevent the soft film barrier agent from sticking to the surface of the polyethylene protective film during the transportation and storage time of the roll-shaped dry film. The protective film can prevent the oxygen from penetrating into the barrier layer and the free radicals in it from accidentally reacting to cause the photopolymerization reaction, and the dry film that has not been polymerized is easily washed away by the sodium carbonate solution.
Wet film: Wet film is a one-component liquid photosensitive film, which is mainly composed of high photosensitive resin, sensitizer, pigment, filler and a small amount of solvent. The production viscosity is 10-15dpa.s, and it has corrosion resistance and electroplating resistance., Wet film coating methods include screen printing, spraying and other methods.
Process introduction:
Dry film imaging method, the production process is as follows:
Pre-treatment-lamination-exposure-development-etching-film removal
Pretreate
Purpose: Remove contaminants such as grease oxide layer on the copper surface and increase the roughness of the copper surface to facilitate the subsequent lamination process
Main raw material: brush wheel
Pre-processing method:
(1) Sandblasting and grinding method
(2) Chemical treatment method
(3) Mechanical grinding method
The basic principle of the chemical treatment method: use chemical substances such as SPS and other acidic substances to uniformly bite the copper surface to remove impurities such as grease and oxides on the copper surface.
Chemical cleaning:
Use alkaline solution to remove oil stains, fingerprints and other organic dirt on the copper surface, then use acid solution to remove the oxide layer and the protective coating on the original copper substrate that does not prevent copper from being oxidized, and finally perform microetching treatment to obtain a dry film Fully roughened surface with excellent adhesion properties.
Control points:
a. Grinding speed (2.5-3.2mm/min)
b. Wear scar width (500# needle brush wear scar width: 8-14mm, 800# non-woven fabric wear scar width: 8-16mm), water mill test, drying temperature (80-90 degree Celsius)
Lamination
Purpose: Paste an anti-corrosive dry film on the copper surface of the processed substrate through hot pressing.
Main raw materials: dry film, solution imaging type, semi-aqueous imaging type, water-soluble dry film is mainly composed of organic acid radicals, which will react with strong alkali to make it organic acid radicals. Melt away.
Principle: Reel dry film (film): first peel off the polyethylene protective film from the dry film, and then paste the dry film resist on the copper clad board under heating and pressure conditions, the resist in the dry film The layer becomes softened by heat, and the fluidity increases. The film is completed by the pressure of the hot pressing roller and the action of the adhesive in the resist.
Three elements of reel dry film: pressure, temperature, transmission speed
Control points:
a. Film sticking speed (1.5+/-0.5m/min), sticking pressure (5+/-1kg/cm2), sticking temperature (110+/--10 degree Celsius), exit temperature (40-60 degree Celsius)
b. Wet film coating: ink viscosity, coating speed, coating thickness, pre-bake time/temperature (5-10 minutes for the first side, 10-20 minutes for the second side)
Exposure
Purpose: Transfer the image on the original film to the photosensitive base plate through the action of the light source.
Main raw materials: The film used in the inner layer of the film is a negative film, that is, the white light-transmitting part is polymerized, and the black part is opaque and does not react. The film used in the outer layer is a positive film, which is the opposite of the film used in the inner layer.
Dry film exposure principle: The photosensitive initiator in the resist in the exposed area absorbs photons and decomposes into free radicals, and the free radicals initiate cross-linking reaction of monomers to form a spatial network macromolecular structure that is insoluble in dilute alkali.
Control points: precise alignment, exposure energy, exposure light ruler (6-8 grade cover film), residence time.
Developing
Purpose: Use lye to wash away the part of the dry film that has not undergone chemical reaction.
Main raw material: Na2CO3
Use the dry film that has not undergone polymerization reaction to be washed away, and the dry film that has undergone polymerization reaction is left on the surface of the board as an anti-corrosion protection layer during etching.
Development principle: The active groups in the unexposed part of the photosensitive film react with the dilute alkali solution to generate soluble substances and dissolve, thereby dissolving the unexposed part, while the dry film of the exposed part is not dissolved.
Control points:
a. Developing speed (1.5-2.2m/min), developing temperature (30+/-2 degree Celsius)
b. Developing pressure (1.4-2.0Kg/Cm2), developer concentration (N2CO3 concentration 0.85-1.3%)
Etching
Purpose: Use the chemical liquid to etch away the exposed copper after development to form the inner layer circuit pattern.
Main raw material: etching solution (CuCl2)
Principle of inner layer etching: In the inner layer pattern transfer process, D/F or ink is used as anti-etching, anti-plating or anti-etching, so most of them choose acid etching (dry film/wet film to cover the surface of the circuit pattern .
Prevent copper etching: other unneeded copper exposed on the substrate will be removed by a chemical reaction to form the required circuit pattern. After the circuit pattern is etched, the dry film/wet film is removed with sodium hydroxide solution).
Control points:
a. Etching: speed, temperature (48-52 degree Celsius), pressure (1.2-2.5Kg/cm2)
b. Film removal: 44-54 degree Celsius, 8-12% NaOH solution
Purpose: Use strong alkali to peel off the anti-corrosion layer protecting the copper surface to expose the circuit pattern.
Technology and R&D: Tengchuangda Circuit has core technology with intellectual property rights. The technology involves high-end products such as high multi-layer boards, ultra-long boards, thick copper boards, high-frequency boards, metal substrates, metal core boards, HDI boards, flexible boards, rigid-flex boards and other high-end products. The interconnection HDI board is in the stage of sample and small batch production, and the production technology of the remaining products is mature, with mass production capabilities, and can be put into production at any time according to changes in market demand.
Products: Electronic products cover multilayer boards, high-density interconnect HDI, high-frequency high-speed boards, flexible circuit boards, rigid-flex circuit boards and other special-specification boards (including: metal substrates, thick copper boards, ultra-long boards, ceramics Board etc.). In 2020, the company's HDI board sales accounted for more than 40% of PCB sales revenue. Tengchuangda Circuits has always adhered to market-oriented production and operation, implemented a differentiated product competition strategy, and focused on the production of products with high technical content and relatively high-end application fields, which to a certain extent avoided the low barriers to entry in the industry. Repeated competition in the field of standardized products.